India becoming world's biggest sulphur dioxide emitter GS: 3 Environment EMPOWER IAS
India becoming world's biggest sulphur dioxide emitter
|
Mains Q:
Q) India is the largest emitter of Sulfur Dioxide in the world. In this context, discuss the impact of sulfure dioxide on human health and enviornment .What steps can be taken to mitigate this problem?
|
|
Table of Content
- In news
- Highlights of the Greenpeace study
- Major hotspots in India
- Major hotspots in world
- Sulphur dioxide significant contributor to air pollution
- Steps taken to mitigate by the government
- Impact: On health, On Environment
- Methodology
- Way ahead
|
In news:
- India emits the most sulphur dioxide in the world as per Greenpeace study

Sulphur dioxide(SO2)
- It is a toxic gas with a pungent, irritating smell. It contributes to acid rain.
- It is released naturally by volcanic activity. It is abundantly available in the atmosphere of Venus.
- Sulphur dioxide is primarily produced for sulfuric acid manufacture.
- Inhaling sulphur dioxide is associated with increased respiratory symptoms and premature death.
- It also weakens the functioning of certain nerves.
- Sources: It is also produced by
- burning coal in thermal power plants and diesel fuels.
- some industrial processes, such as the production of paper and smelting of metals.
- reactions involving Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S) and oxygen.
- The roasting of sulphide ores such as pyrite, sphalerite, and cinnabar (mercury sulphide)
- Natural sources of sulphur dioxide include geothermal activity.

Key highlights of the Greenpeace report:
- India is the largest emitter of sulphur dioxide in the world, with more than 15% of all the anthropogenic sulphur dioxide hotspots detected by the NASA OMI (Ozone Monitoring Instrument) satellite.
- Five of the top 10 SO2 emission hotspots from coal/power generation industry across the world are in India, finds a Greenpeace study
- The vast majority of coal-based power plants in India lack flue-gas desulphurisation technology to reduce air pollution.
- Air pollutant emissions from power plants and other industries continue to increase in India, Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- Despite 75 per cent drop in SO2 emissions, China's air quality continues to cause significant health problems as SO2 contributes to only about 10-20 per cent of air particles that cause haze.
- Despite 75 per cent drop in SO2 emissions, China's air quality continues to cause significant health problems as SO2 contributes to only about 10-20 per cent of air particles that cause haze.
- By contrast, India's sulphur dioxide emissions increased by 50 per cent over the past decade as India opened its largest coal-fired power plant in 2012 and has yet to implement emission controls.
The Methodology used:
- In order to generate an accurate profile of emissions over India and China, the researchers combined emissions data generated by using two different methods.
• The first method was the collection of estimated emission amounts from inventories of the number of factories, power plants, automobiles and other contributors to sulphur dioxide emissions.
The second data source was the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA's Aura satellite, which detects a variety of atmospheric pollutants including sulphur dioxide.
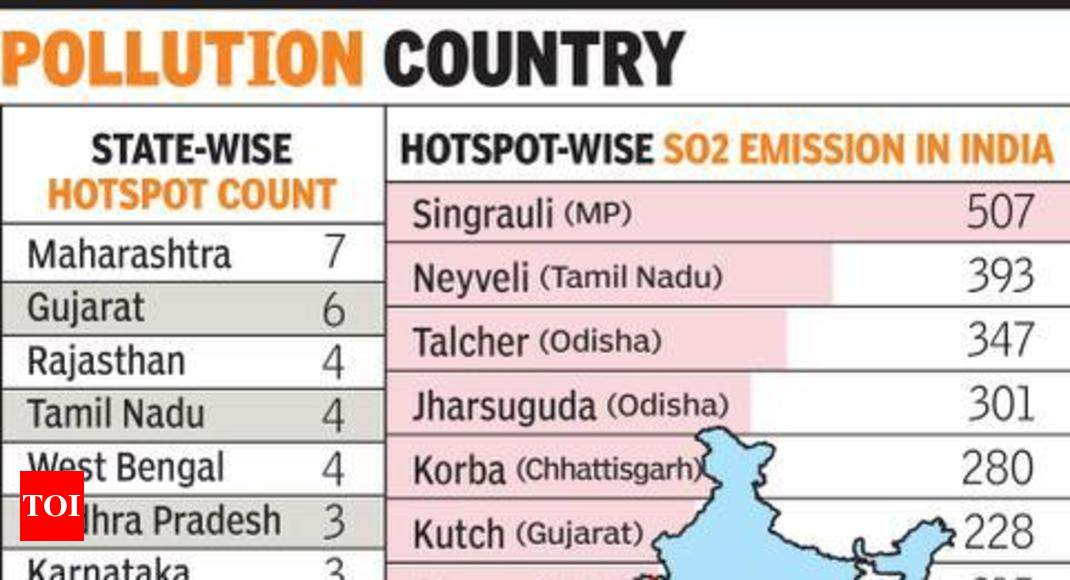
Major hotspots in India
- The Singrauli, Neyveli, Talcher, Jharsuguda,Korba, Kutch, Chennai, Ramagundam, Chandrapur and Koradi thermal power plants or clusters are the major emission hotspots in India.
- The report also includes NASA data on the largest point sources of sulphur dioxide.
- As per country-wise world rankings, India was found at the top position in emitting SO2 as it has the maximum hotspots.
Hotspots in the world
- The largest sulphur dioxide emission hotspots have been found in Russia, South Africa, Iran, Saudi Arabia, India, Mexico, United Arab Emirates, Turkey and Serbia.
- Air pollutant emissions from power plants and other industries continue to increase in India, Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- Of the world’s major emitters, China and the United States have been able to reduce emissions rapidly. They have achieved this feat by switching to clean energy sources.
- China has achieved success in reducing Sulfur dioxide by dramatically improving emission standards and enforcement for sulphur dioxide control.

Sulphur dioxide significant contributor to air pollution
- The report said SO2 emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution.
- The largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and other industrial facilities.
- Air pollution is a huge public health concern, with 91 percent of the world's population living in areas where outdoor air pollution exceeds guideline limits by the World Health Organization (WHO) and as a result, 4.2 million people die prematurely every year.

Impact of sulfur dioxide:
On health
- Sulphur dioxide can cause respiratory problems such as bronchitis, and can irritate your nose, throat and lungs.
- It may cause coughing, wheezing, phlegm and asthma attacks.
- The effects are worse when you are exercising.
- Sulphur dioxide has been linked to cardiovascular disease.
- Sulphur dioxide can form secondary particles (sulphates) that cause haze and reduce visibility.
- SOx can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles. These particles contribute to particulate matter (PM) pollution.
- Small particles may penetrate deeply into the lungs and in sufficient quantity can contribute to health problems.
On Environment:
- Sulphur dioxide is an air pollutant that causes acid rain, haze and many health-related problems.
- Acid rain is a major problem in the northern hemisphere where trees and whole forests have been affected.
- sulphur dioxide deposition can affect vegetation around industrial discharges and in cities.
- Lichens are good bio-indicators of pollution as they do not like to grow where there is sulphur dioxide in the air.
- Corrode building materials and paints.
- cause deforestation
Steps taken to mitigate:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change introduced, for the first time, sulphur dioxide emission limits for coal-fired power plants in December 2015. But the deadline for the installation of flue-gas desulphurisation (FGD) in power plants has been extended from 2017 to 2022.
- At the request of the Ministry of Power and power plant operators, this was later extended till December 2019 for power plants in Delhi-NCR and till 2022 for some other power plants across the country through a Supreme Court order
- Rising emissions from coal-based power plants have made India overtake China in sulphur dioxide emissions.
At global level:
- United States Environmental Protection Agency(EPA) took national and regional rules to reduce emissions of SO2 and pollutants that form sulfur oxides (SOx) will help state and local governments meet the Agency’s national air quality standards.
- EPA identifies areas where the air quality does not meet EPA SO2 standards. For these areas, state, local, and tribal governments develop plans to reduce the amount of SO2 in the air.
Way ahead:
- Implementing national fuel quality standards;
- Supporting the implementation of tighter vehicle emission standards; and
- Promoting alternative fuels.
- Shift fossil fuel plants to lower sulfur fuels.
- Shift to nuclear generation as rapidly as possible since no sulfur oxide (or particulate) is emitted from nuclear plants;
- One option is to use coal that contains less sulfur and “wash” the coal to remove some of the sulfur.
Source)
indianexpress.com/article/explained/india-biggest-emitter-of-sulphur-dioxide-report-using-nasa-data-5918283/






